In order to understand the Indian government’s take on cryptocurrency, all you have to do is read this statement made by Mr. Narendra Modi at the Sydney Dialogue last week – “It is important that all democratic nations work on this (cryptocurrency) and ensure that it does not end up in the wrong hands, which can spoil our youth”.
The Indian Government plans on introducing the eagerly anticipated ‘The Cryptocurrency and Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill 2021’ in Parliament during the ongoing Winter Session1.
The Bill is widely expected to be introduced in the coming days, and the Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman on November 30th, 2021 made a categoric statement in the Rajya Sabha that a new crypto bill will be introduced in the House after approval from the Cabinet.
The Lok Sabha Bulletin said the bill aims “to create a facilitative framework for creation of the official digital currency to be issued by the Reserve Bank of India”.
“The bill also seeks to prohibit all private cryptocurrencies in India,” the bulletin said. “However, it allows for certain exceptions to promote the underlying technology of cryptocurrency and its uses”.
The term private cryptocurrencies is noteworthy for the simple reason that there has been news coming in about governments coming up with their own official cryptocurrency. These cryptocurrencies are known as CBDCs or Central Bank Digital Currencies2. There could be a possibility that this CBDC, the virtual form of a country’s fiat currency, is deemed as the only public cryptocurrency and all others be classified as private cryptocurrencies.

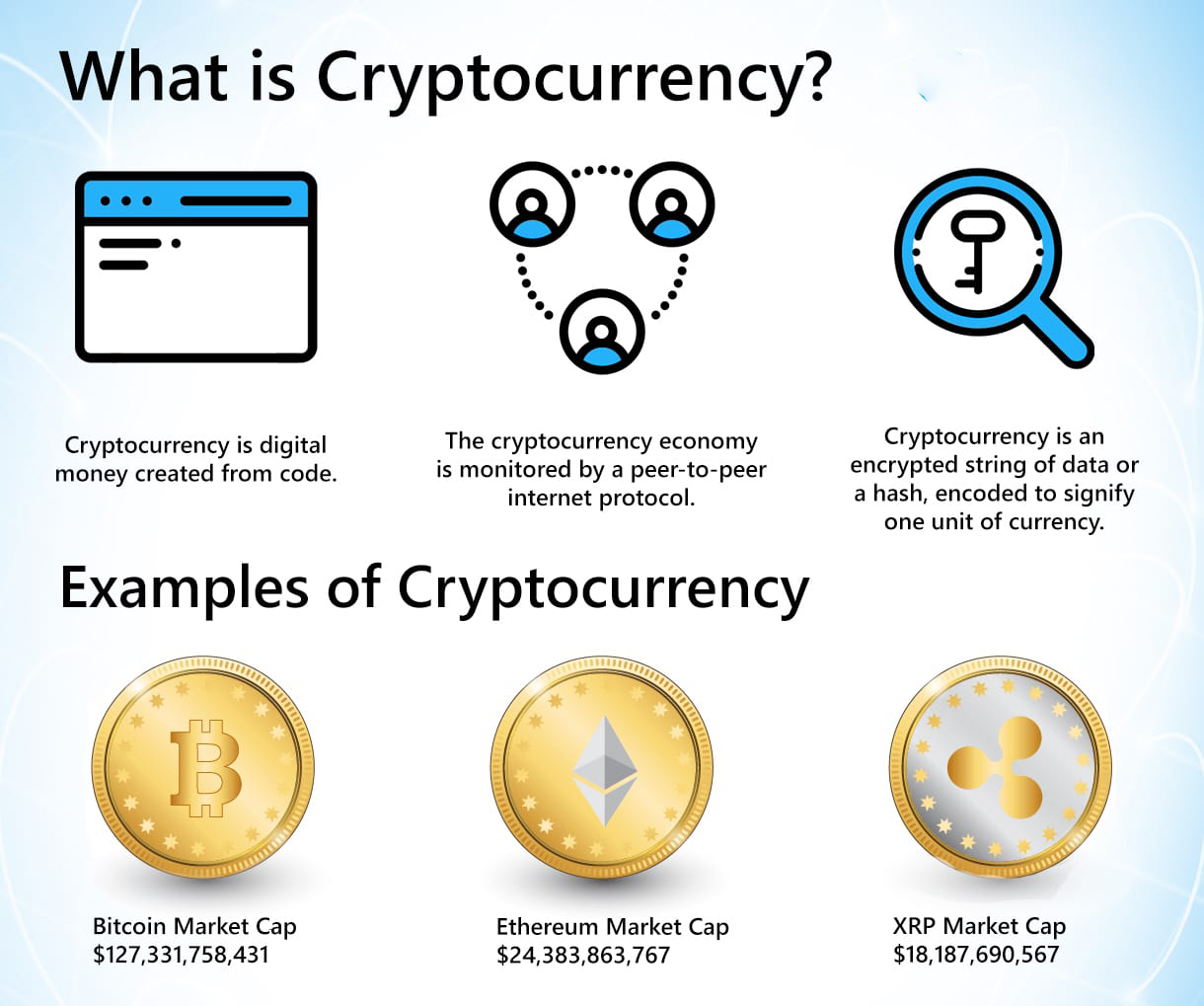
What is a cryptocurrency ?
A cryptocurrency3 is protected by cryptography4. This refers to a method of encrypting communication using a code so that it can be only be accessed by people for whom it is intended. Cryptocurrency is produced by “mining” it:
2. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/central-bank-digital-currency-cbdc.asp
3. https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/cryptocurrency.asp
4. https://www.kaspersky.com/resource-center/definitions/what-is-cryptography
powerful computers are deployed to break these codes, for which they are rewarded with the currency.
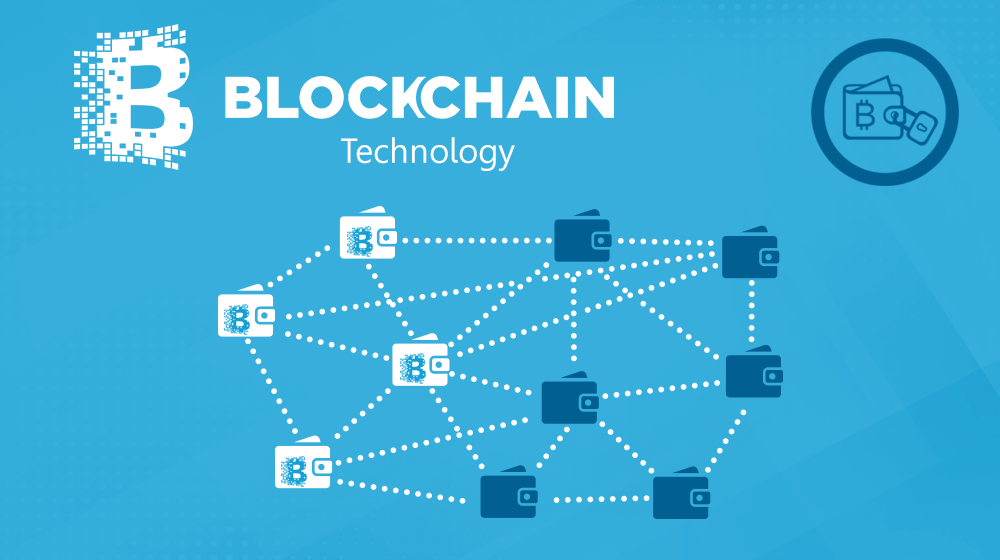
Blockchain is the technology that enables the existence of cryptocurrency (among other things). A blockchain is a decentralized ledger of all transactions across a peer-to-peer network. Using this technology, participants can confirm transactions without a need for a central clearing authority. Potential applications can include fund transfers, settling trades, voting, and many other issues5.
Each block contains only some information. Once data is added to one block, it becomes extremely difficult to change it, since all subsequent blocks are connected and would have to be changed too. As a consequence, cryptocurrency is considered to be almost impossible to duplicate6.
The recent history of cryptocurrency in India
In 2018, citing risks associated with virtual currencies, the Reserve Bank of India issued a circular7 that prohibited banks and financial institutions from dealing in virtual currencies or providing services to any person or entity dealing in virtual currencies. This, in effect, banned the use of cryptocurrency in India.
Two years later in March, 2020, the Supreme Court struck down this circular on grounds of proportionality. While it acknowledged that the Reserve Bank has the power to regulate virtual currencies, which would include cryptocurrencies, the court said that the regulation has to be proportionate to the risk of damage posed8.
In the year 2019, the Inter-ministerial Committee issued its final report, along with a proposed law titled Banning of Cryptocurrency & Regulation of Official Digital Currency Bill, 20199, which sought a complete ban on cryptocurrency. It said that no person should “mine, generate, hold, sell, deal in, issue, transfer, dispose of or use” cryptocurrency in India. This bill however, after having been widely criticized, was never tabled.
6. https://www.ibm.com/in-en/topics/what-is-blockchain
7. https://rbidocs.rbi.org.in/rdocs/notification/PDFs/NOTI15465B741A10B0E45E896C62A9C83AB938F.PDF
8. https://main.sci.gov.in/supremecourt/2018/19230/19230_2018_4_1501_21151_Judgement_04-Mar-2020.pdf
9. https://prsindia.org/files/bills_acts/bills_parliament/1970/Draft%20Banning%20of%
20Cryptocurrency%20&%20Regulation%20of%20Official%20Digital%20Currency%20Bill,%202019.pdf